01 AWS Networking Basics
AWS Networking Services
Network foundations
- VPC
- Transit gateway
- Private link
Hybird connectivity
- Direct connection
- Cloud WAN
- Client VPN
- Site-to-Site VPN
Edge networking
- CloudFront
- Route53
- Global Accelerator
Application networking
- API Gateway
- App Mesh
- Cloud Map
Networking security
- Firewall Manager
- Shield
- Network Firewall
- WAF
Network Concepts
Network design pattern
- point to point
- Bus
- Tree
- Hub and Spoke
- Mesh
- Ring
- Hybrid
Protocol
- Network management protocols
- HTTP
- TCP
- UDP
- IRC(Internet Relay Chat): is a text-based communication protocol
- Network communication protocols
- SNMP
- ICMP
- Network security protocols
- SSL
- SFTP
- HTTPS
IPv4
32 bit digis, 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255
IPv6
Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR)
- CIDR management ip address space
- CIDR reduce the number of table entries
Subnetting
- Host and network
- class A 205.0.125.100, network : 205, host :0.125.100.
- class B 205.0.125.100, network : 205.0, host : 125.100.
- class C 205.0.125.100, network : 205.0.125, host : 100.
Subnet mask
For determine the number of IP address by given local network requires based on the default subnetwork.
Accessing data
- Network attached storage(NAS): Elastic file system, Amazon FSx.
- Storage area network(SAM): Amazon Elastic Block Storage(EBS).
AWS Implementation
Open Systems Interconnect(OSI) model
The OSI model contains 7 layers: physical layer, data link layer, network layer, transport layer, session layer, presentations layer, and application layer. These 7 layers are the networking stack, which is the software that completes each function.
TCP/IP
-
Link MAC address
-
Internet IPv4
-
Transport TCP
-
Application HTTP
AWS Network Connectivity Options
Understant Connectivity Concepts
Multi-tier architecture
- Presentation tier
- Application or logic tier
- Data tier
Multi-VPC architecture
For Create connections between application for distributed applications
Hight avaliability
A network that is designed to avoid loss of communications between established network endpoints.
by implementation of :
- redeundant components
- parallel components
- distribute traffic load
- elimination of single point of faliure
Hybrid networks
At least two indepentdent networks communicate with each other.
High performance
Privide fastest experience by guiding a packet of data along the shortest path with minimal delay.
Understant AWS Network Service Offerings
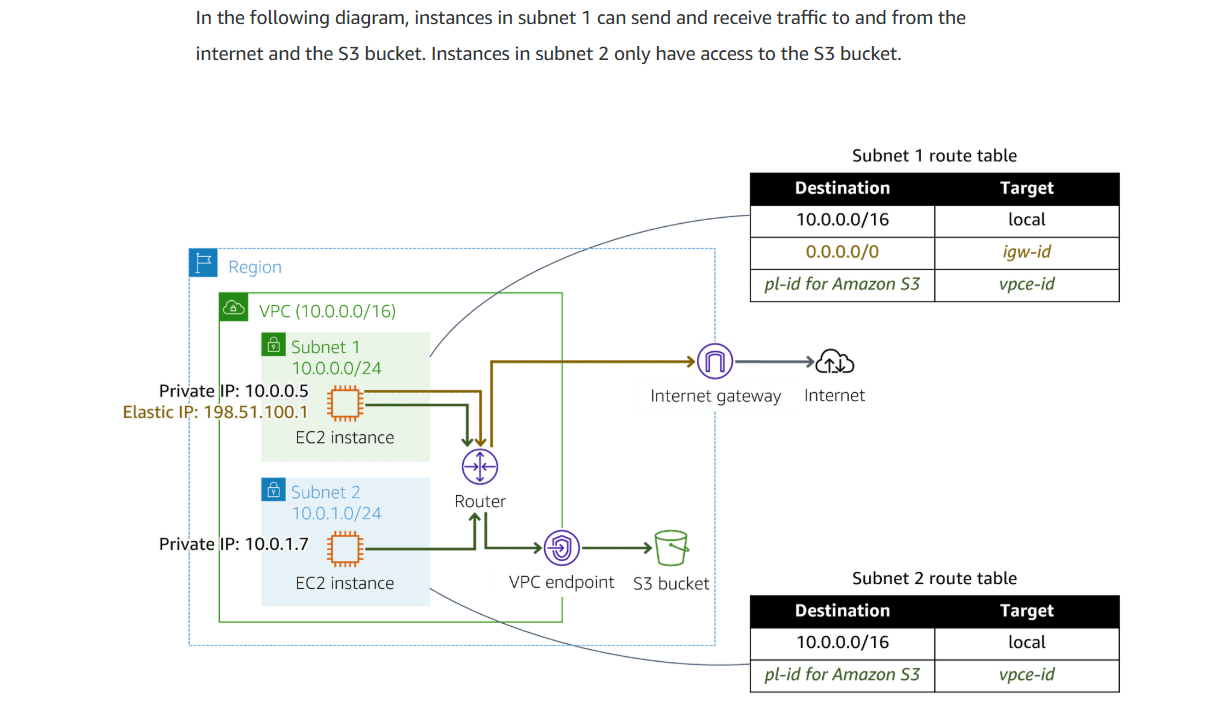
Virtual private cloud(VPC) endpoint and AWS PrivateLink
-
Gateway VPC endpoints
A gateway VPC endpoint targets specific IP routes in a VPC route table in the from of a prefix list.
-
Interface endpoints
Powered by privateLink, an interface endpoint is an elastic network interface with a private IP address from the IP address range of the subnet. as an entry point for traffic.
-
Gateway Load Balancer endpoint
A gateway load balancer endpoint is an elastic network interface with a private IP address from the IP address range of the subnet.traffic and route it to a service that configured using Gateway Load balancer.
-
What is AWS PrivateLink

- Provite connection between VPCs and supported AWS Services.
- Avoids exposing traffic to the public internet.
Benefits :
- Security
- Simplification
- Capabilities
Considerations :
- Does not support IPv6.
- Service Provider will never see the IP address of the customer or service consumer.
- Endpoint services cannot be tagged.
- The private Domain Name System (DNS) of the endpoint does not resolve outside of the VPC.
- Availability Zone names in a customer account might not map to the same locations as Availability Zone names in another account.
-
DNS DNS Will be created for interface endpoint.
-
Endpoint-specific regional DNS hostname.
vpce-0fe5b17a0707d6abc-29p5708s.ec2.us-east-1.vpce.amazonaws.com
-
Zonal-specific DNS hostname.(include avaliable zone)
vpce-0fe5b17a0707d6abc-29p5708s-us-east-1a.ec2.us-east-1.vpce.amazonaws.com
-
Private DNS hostname.
Create for zonal-specific or regional-specific DNS into a friendly hostname.
myservice.example.com
-
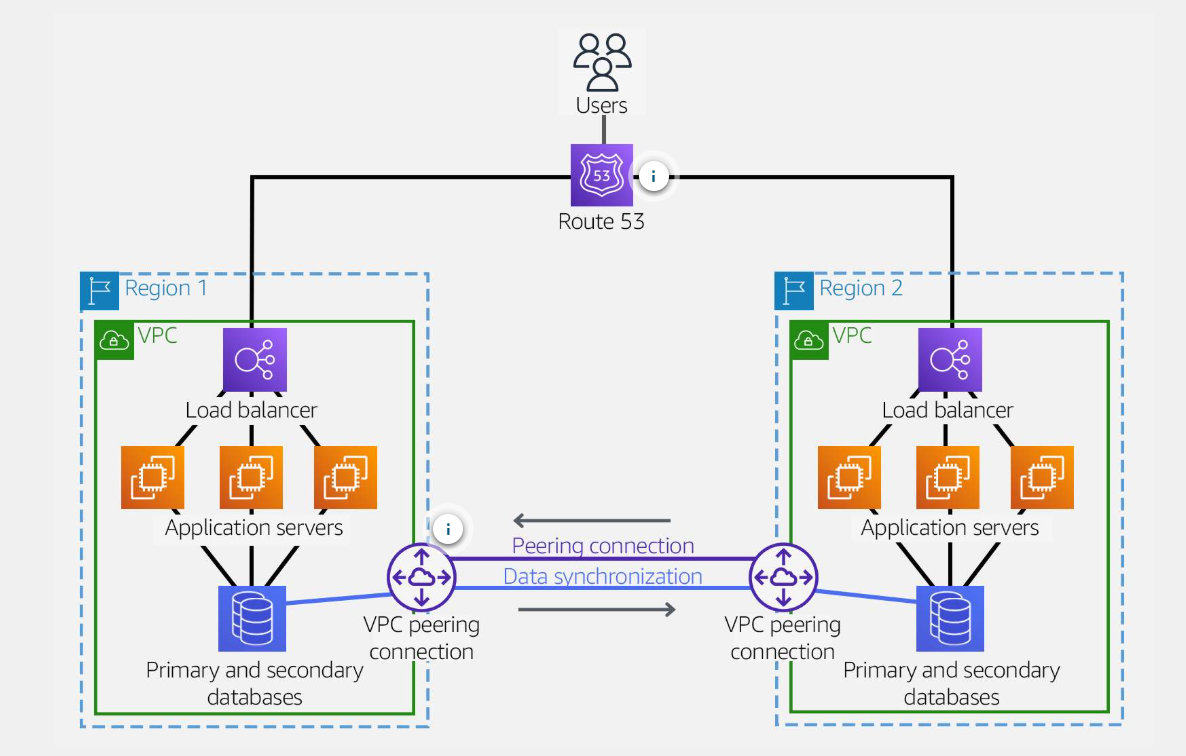
VPC peering
A network connection between two VPCs and route traffic privately.
-
Benefits :
- Highly avaliable.
- does not relay on a separate pice of physical hardware.
- no bandwidth bottleneck or single point of failure of communication.
-
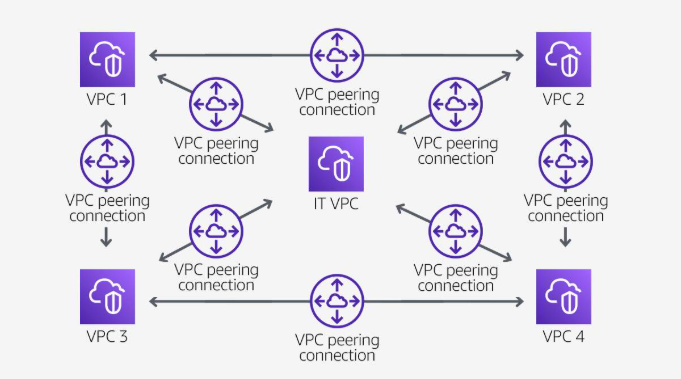
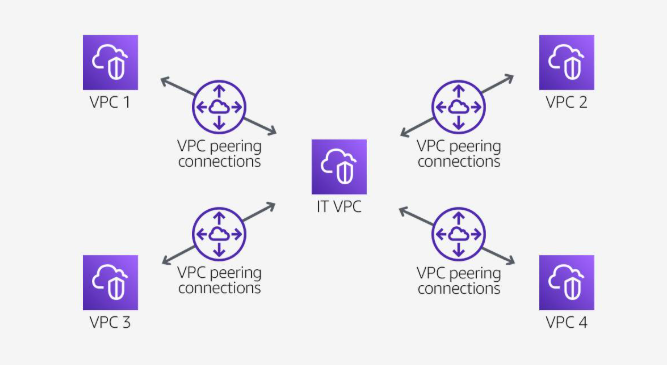
Peering scenarios
- Full Sharing of resources between all VPCs
- Partial sharing of centralized resources
- Full Sharing of resources between all VPCs
-
Non-valid peering configurations
- Overlappiong CIDR blocks
- Transitive peering
- Edge-to-edge routing through a gateway or private connection
If either VPC in a peering relationship has one of the following connections, you cannot extend the peering relationship to that connection:
A VPN connection or a Direct Connect connection to a corporate network An internet connection through an internet gateway
An internet connection in a private subnet through a NAT device
A gateway VPC endpoint to an AWS service, for example, an endpoint to Amazon S3
AWS Direct Connect
Direct connection privides a private, reliable connection to AWS private data center or office.
-
Speed
-
All connections must be decicated connections and have a port speed of 1Gbps, 10 Gbps, 100Gbps.
-
All connection in the LAG must use the same bandwidth.
-
A LAG can have maximum of two 100-Gpbs connections or 4 connection port speed less than 100-Gpbs.
-
All connection in the LAG must terminate at the same Direct Connect endpoint.
-
when Create a LAG, you can download the letter of Aithorization and connecting Facility Assignment(LOA-CFA) for each physical connection.
-
-
Network Requirement
- Your network is co-located with an existing Direct connect location.

- You are working with a Direct Connect Partner.
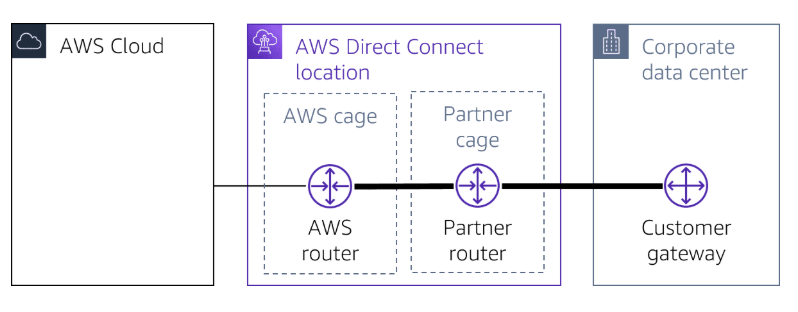
- You are working with an independent service provider to connect to Direct Connect.
- Your network is co-located with an existing Direct connect location.
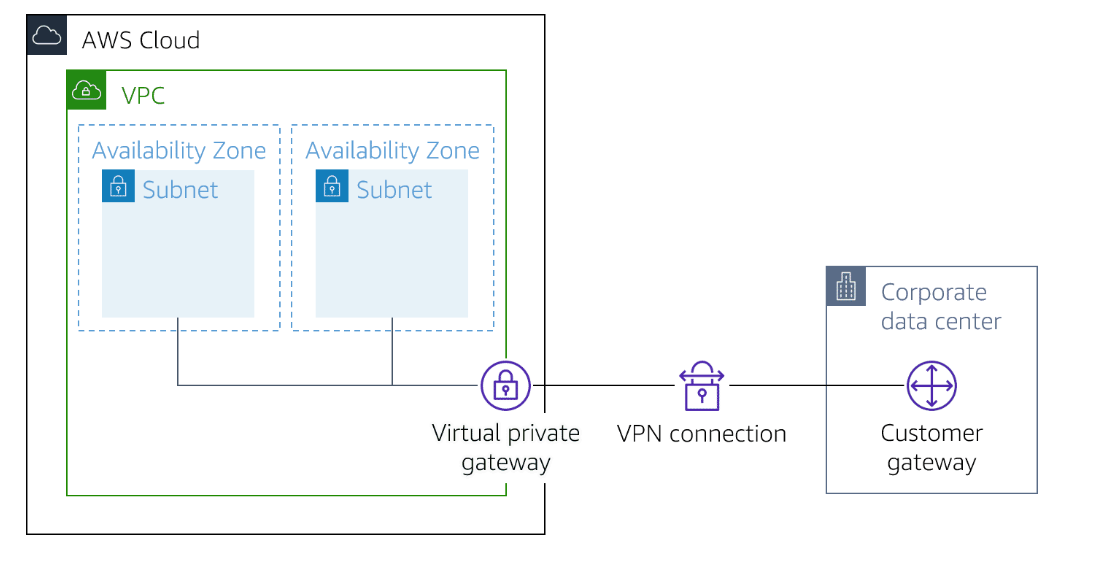
AWS Site-to-Site VPN and AWS Client VPN
-
Enables you to securely connect your on-premises network to Amazon VPC.
-
Enables you to securely connect users to AWS or on-premises network.
-
Gateways
-
Customer gateway
A resource you create and configred in AWS that represents your on-premise gateway device.
-
Customer gateway device
A customer gateway device is a physical device or software application on your side of the AWS Site-to-Site VPN connection.
-
Virtual private gateway
A virtual private gateway is the VPN connector on the Amazon side.
-
Transit gateway
A transit gateway is a transit hub that can be used to interconnect your VPCs and on-premises network.
-
-
Limitations
-
IPv6 traffic is partially supported.(IPv6 outter tunnel connection not supported)
-
Does not support Path MTU discovery.
-
Maximum packets per second(PPS) per VPN tunnel is 140,000.
-
...
-
-
Monitoring
Use Cloud Watch, not support AWS Classic VPN connections.
-
Client VPN
Based on OpenVPN, Client VPN is a managed client-based VPN service that let you securely access your AWS resources and resources in your on-premises network.
- Client VPN endpoint
Your Client VPN administrator creates and configures a client VPN endpoint in AWS.
- VPN client application
Software that use to connect to the Client VPN endpoint and establish a secure VPN connection.
- Client VPN endpoint configuration file
A configuration file that is provided to you by your Client VPN administrator.
Limitations:
- IPv6 is no supported.
- Clinet CIDR ranges must have a block size of at least /22 and must not be greater than /12.
Monitoring : Could Watch
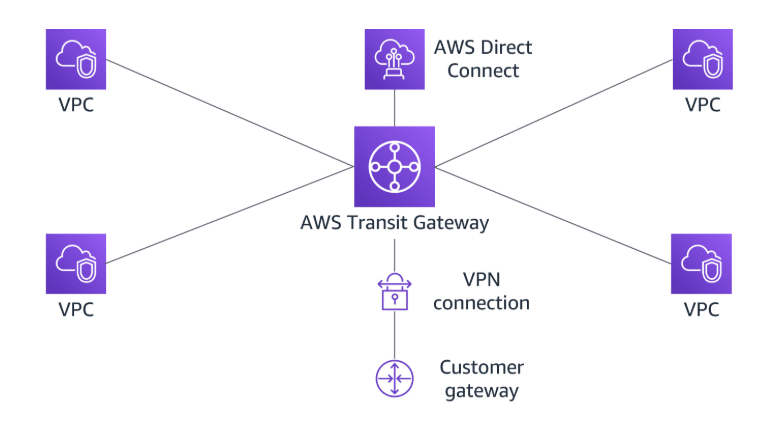
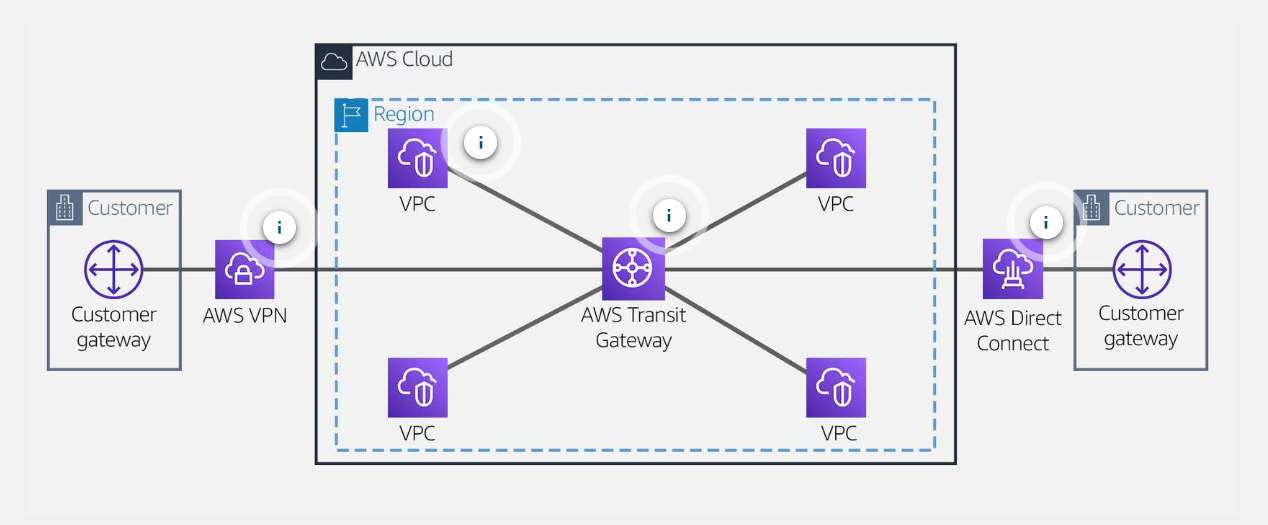
AWS Transit Gateway
AWS Transit Gateway is a highly avaliable and scalable service that provide interconnectivity bwtween VPCs and on-premises network.
-
Attachments
AWS Transit Gateway supports the following connections:
- One or more VPCs
- A compatible Software-Defined Wide Area Network(SD-WAN) application.
- A Direct Connect gateway.
- A peering connection with another transite gateway.
- A VPN connection to a transit gateway.
-
AWS Transit Gateway MTU
AWS Transit Gateway supports an MTU of 8500 bytes for :
- VPC connections
- Direct Connect connections.
- Connections to other transit gateways.
- Peering connections.
-
AWS Transit Gateway route table
A route table includes dynamic and static routes that decide the next hop basedon the destination IP address of packet.
-
Associations
Each attachment is associated with exatly one route table. each route table can be associated with zero to many attachments.
-
Route propagation
A VPC, VPN connection or Direct Connect gateway can dynamically propagate routes to a transit gateway route table. Whit a Direct Connect attachment, the routes are propagated to transit gateway route table by default.
Whit a VPC, you must create static routes to send traffic to the transit gateway.
With a VPN connection or a Direct Connect gateway, routes are propagated from the transit gateway to your on-premises router using BGP.
With a peering attachment, you must create a static route in the transit gateway route table to point to the peering attachment.
-
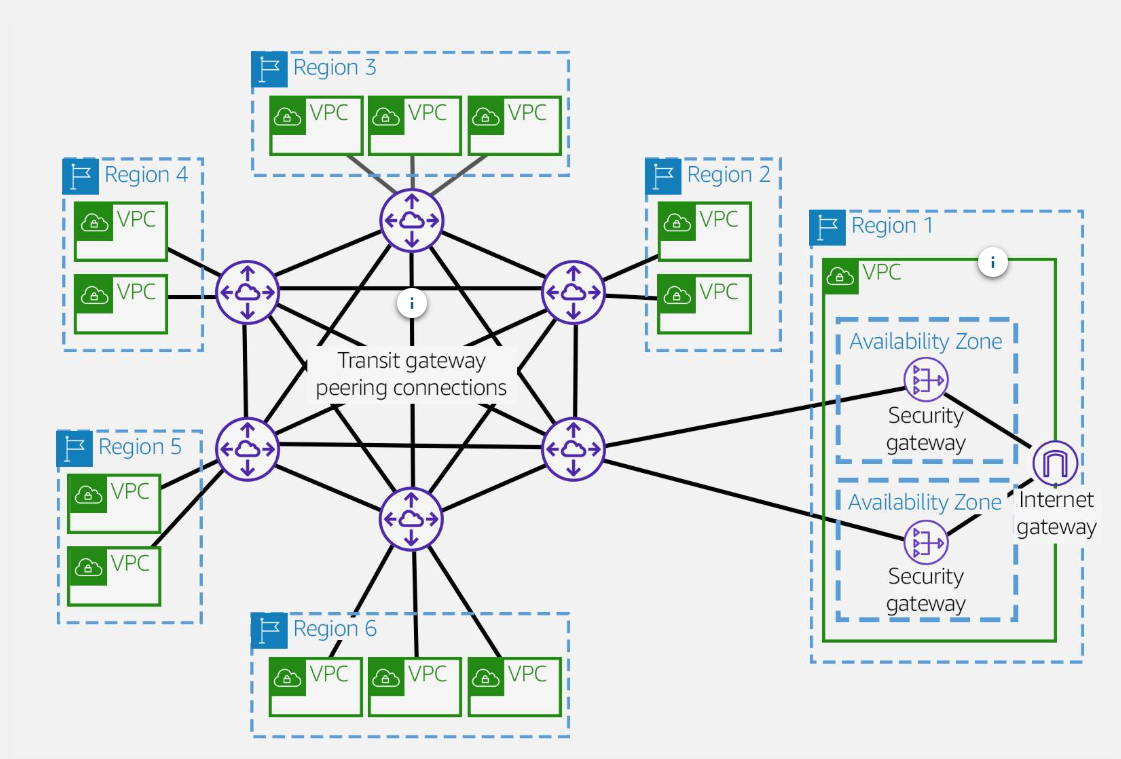
AWS Transit Gateway inter-regional peering
-
VPC peering
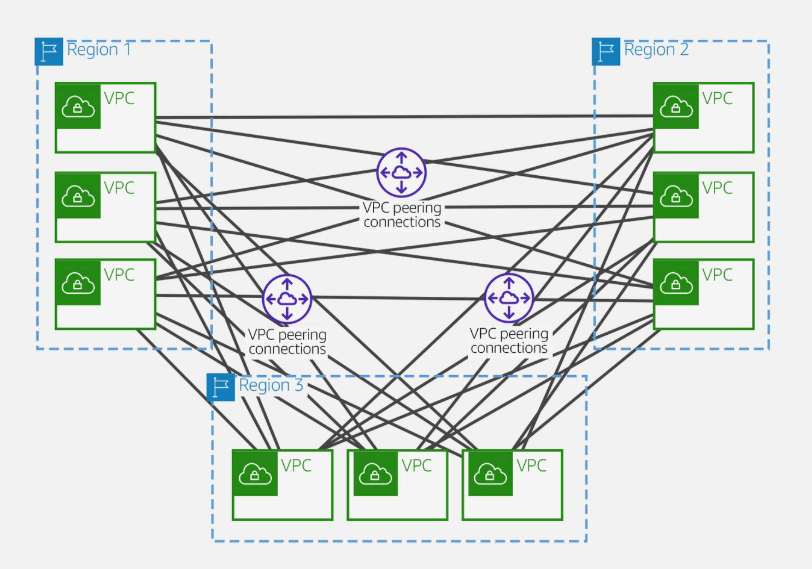
-
transit gateway peering
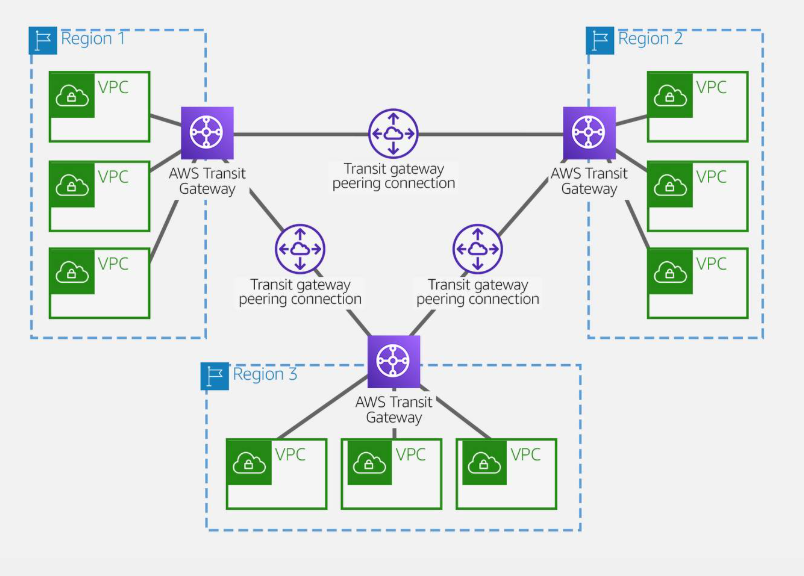
-
Hub and Spoke
Hybird network
Cross-regional VPC peering
Exploring Design Patterns
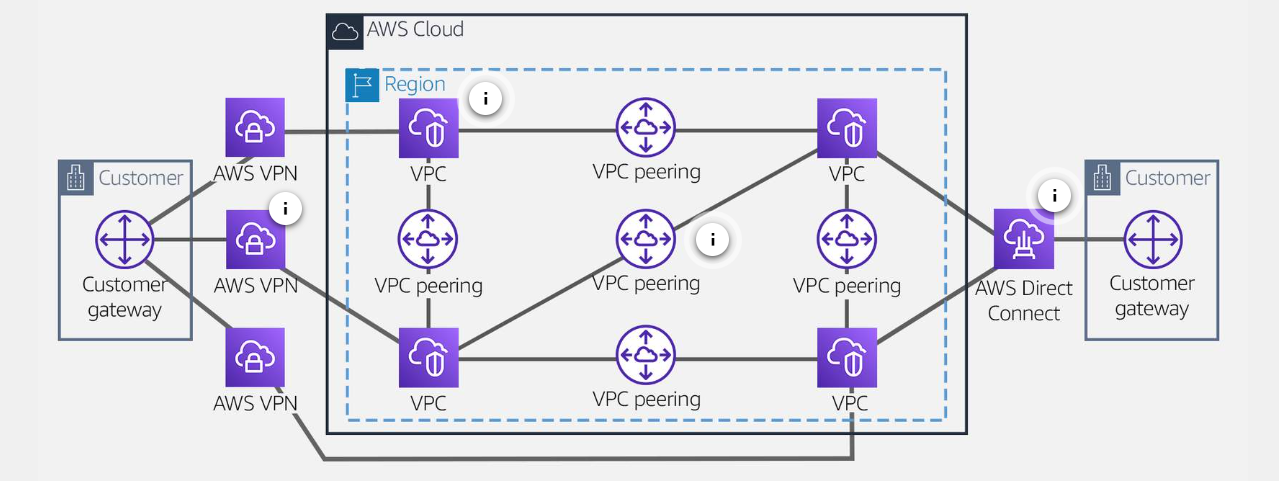
Simplifying Multi-VPC Routing
- Before
- After
Resilient Hybird Networks
- Before
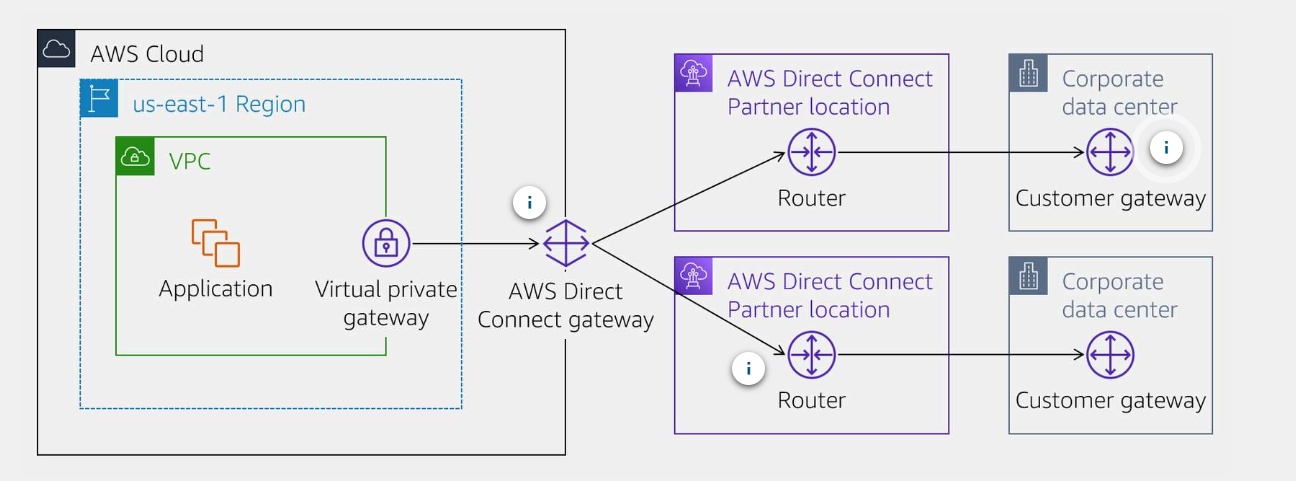
- After

Regional High Avaliability
AWS Transit Gateway Peering