Cryptography
Hash Functions
- One-way function - cannot be reversed
- Fixed length output
public void OnGet()
{
var plainText = "Hello World!";
// MD5 Hash, create an instance of the MD5 hash algorithm
SHA512 hashSvc = SHA512.Create();
// Compute the hash value, returns a byte array
byte[] hash = hashSvc.ComputeHash(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(plainText));
// Convert the byte array to a hexadecimal string, because the hash is a byte array
var hex = BitConverter.ToString(hash).Replace("-", "").ToLower();
}
Encryption and decryption
Symmetric Encryption
- Encryption and decryption use the same key
- Faster than asymmetric encryption
- Key management is difficult
Symmetric algorithms
- .NET Symmetric algorithm are "block ciphers"
- Mode : ECB, CBC, CFB, OFB, CTR, GCM
- IV (Initialization Vector)
- Ramdom value that is used to initialize the encryption algorithm
- Does not need to be secret
- Must be unique for each message
public string IV { get; set; }
public string CipherText { get; set; }
public string OriginalText { get; set; }
private Aes CreateCipher()
{
// Create an instance of the AES algorithm
Aes cipher = Aes.Create(); // Defaults - KeySize = 256, BlockSize = 128, Mode = CBC, Padding = PKCS7, IV = Random
// cipher.Padding means that the data is padded to the block size, PaddingMode is a enumeration that specifies the type of padding to apply when the message data block is shorter than the full number of bytes needed for a cryptographic operation.
cipher.Padding = PaddingMode.ISO10126;
// use a constant key for encryption
cipher.Key = conversions.HexToByteArray("2B7E151628AED2A6ABF7158809CF4F3C");
return cipher;
}
public async Task<string> OnGetEncryptAsync()
{
Aes cipher = CreateCipher();
// Encrypt the data
IV = Convert.ToBase64String(cipher.IV);
// Create an encryptor for the cipher to use
ICryptoTransform encryptor = cipher.CreateEncryptor();
byte[] plainText = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("Hello World!");
// Perform the encryption, returns a byte array, transformFinalBlock is used to process the last block of data
byte[] cipherText = encryptor.TransformFinalBlock(plainText, 0, plainText.Length);
CipherText = Convert.ToBase64String(cipherText);
return CipherText;
}
public async Task<string> OnGetDecryptAsync()
{
Aes cipher = CreateCipher();
cipher.IV = Convert.FromBase64String(IV);
ICryptoTransform decryptor = cipher.CreateDecryptor();
byte[] cipherText = Convert.FromBase64String(CipherText);
byte[] plainText = decryptor.TransformFinalBlock(cipherText, 0, cipherText.Length);
OriginalText = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(plainText);
return OriginalText;
}
Asymmetric Algorithms
-
Utilizes two complimentary keys (public and private)
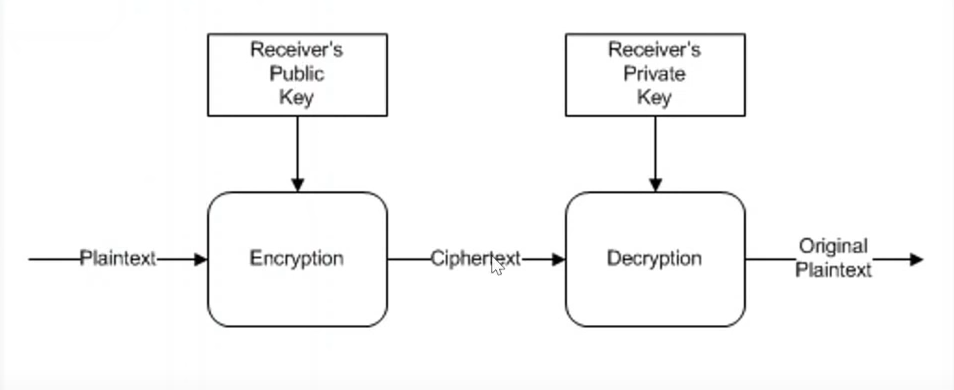
-
Generally slower than symmetric algorithms
-
Often use asymmetric to encrypt a "session" symmetric key
-
Abstract base class: RSA, ECDiffieHellman, ECDsa
public string OriginalText { get; set; }
public string CipherText { get; set; }
public string plainText { get; set; }
private RSA CreateCipher()
{
// RAS is an abstract class, so we use the Create method to create an instance of the RSA algorithm
RSA cipher = RSA.Create(); // Defaults - KeySize = 2048
// Read the public and private keys from the XML files
cipher.FromXmlString(System.IO.File.ReadAllText("rsa-private.xml"));
return cipher;
}
public async Task<string> OnPostEncryptAsync()
{
RSA cipher = CreateCipher();
// Encrypt the data
byte[] data = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(plainText);
byte[] cipherText = cipher.Encrypt(data, RSAEncryptionPadding.Pkcs1);
CipherText = Convert.ToBase64String(cipherText);
return CipherText;
}
public async Task<string> OnPostDecryptAsync()
{
RSA cipher = CreateCipher();
byte[] cipherText = Convert.FromBase64String(CipherText);
byte[] data = cipher.Decrypt(cipherText, RSAEncryptionPadding.Pkcs1);
OriginalText = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(data);
return OriginalText;
}